EC2
- Stands for Elastic Compute Cloud.
- Foundation of cloud computing.
- Falls under IaaC category.
- Configurable OS, CPU, RAM, Storage, Network, Firewall.
- Optional: Specify a bootstrap script.
- Install updates/softwares/libraries.
- Download something from internet.
- AKA “User Data Script”.
- Executes commands as root user (No need to prepend your commands with
sudo).
-
Optional: Create or specify which key pair you’ll be using to connect to the EC2 instance via SSH.
- Available options: ED25519, RSA.
- AWS will copy the pub key automatically inside the EC2 instance.
- AWS will create a default username for us called
ec2-user,root,ubuntu, and a few others. It depends on the distribution you choose (learn more). - Do not forget to change the
.pemfile access permissions to “0400”.
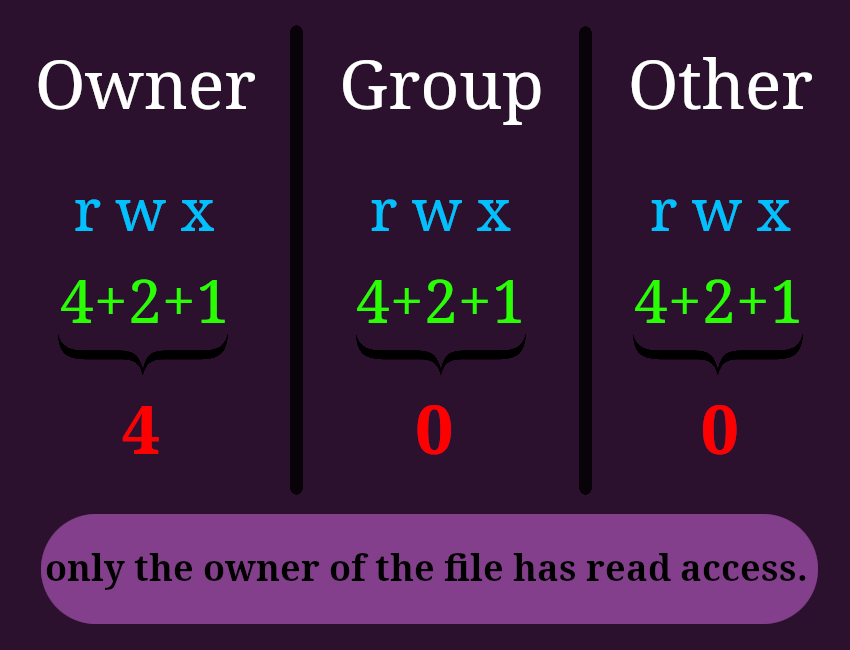
-
We can select different OS images:
- E.g. AMI, Ubuntu, Windows, macOS, Debian.
-
AMI Comes with preinstalled
aws.[!CAUTION]
Do not configure your
awshere (aws configure), It poses a lot of security risks and hard to debug. Because we cannot track exactly who, with which access rights did what. -
AMI:
- Stands for Amazon Machine Image.
- They’re customized EC2 instances.
- They’re bound to a region.
-
To create one:
- Launch an EC2 instance.
- Customize it: do whatever you need inside it/through “user data”.
-
Stop it (For data integrity’s sake).
[!CAUTION]
If you’re EC2 instance cannot be stopped then when you wanna build AMI you need to check “No Reboot” so that the machine stays up.
- Build AMI (this step creates snapshots).
- EC2 image builder:
- Automates:
- AMI creation.
- Maintenance (update OS, libs, etc).
- Validation (it is working the way it is intended to).
- This is a free separate service.
- We’ll pay of course for the underlying resources that will be used.
- Automates:
- We can use IAM roles to let our EC2 instance work with other services.
- Create a role with necessary permissions.
- Assign the role to the EC2 instance via AWS console:
- Open your console.
- Select the EC2 instance you wanna assign the role to it.
- “Actions -> Security -> Modify IAM role”.
EC2 service components
- EC2 instances: Essentially leased virtual machines.
- EBS - Elastic Block Storage: stores data on virtual drives.
- ELB - Elastic Load Balancer: balances load on EC2 instances.
- ASG - Auto Scaling Group: Scale EC2 instances.
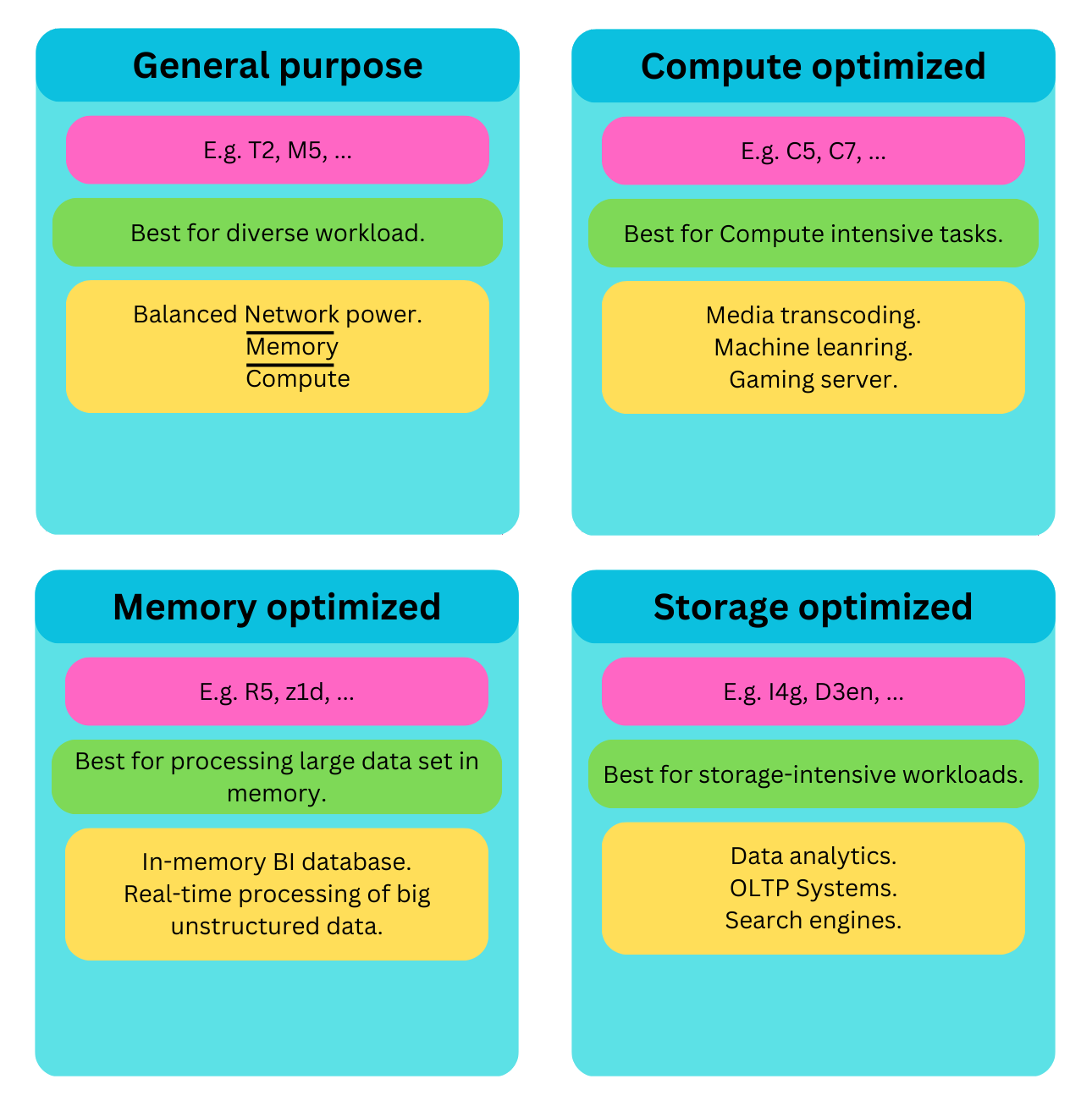
Most used EC2 instance types
Purchasing options for EC2 instances
| Type | Description | Good for |
|---|---|---|
| On-demand | Pay for compute capacity by the second. |
|
| Reserved Instances | Runs for a specific period. |
|
| Convertible Reserved Instance | Similar to reserved instances. |
When you probably need to change instance:
|
| Saving Plans | You commit to a consistent amount of usage ($/h). |
|
| Spot Instances |
|
When your workload has the attribute of being resilient to failure. |
| Dedicated Host | A complete, actual server. |
|
| Dedicated Instances | Dedicated hardware, though it might be shared with other EC2 instances from the same account. | When you need dedicated hardware. |
| Capacity Reservation |
|
|
Features
-
Security groups (SG):
- It is like a virtual firewall.
- Filters and manages traffics that reaches (Go in (inbound) or out(outbound)) EC2 instance.
- Can reference each other.
- KISS: Do not overuse it.

[!TIP]
How to debug your network issues:
- Got timeout error? security group is involved directly.
- Got a connection refused error? Check your own application.
Define a separate security group for SSH access and reuse it wherever needed.
-
# Elastic Block Store (EBS):
- Attachable network drive (they ain’t physical).
- Persistent block storage.
- Limitations:
- Performance (for higher performance use EC2 instance store).
- Mountable to one instance at a time (for being able to mount one storage to multiple EC2 instance look at EFS).
- Bound to a specific AZ (use EFS if you need to share same storage across AZs).
-
4 different volume types:
SSD HDD gp2/gp3 io1/io2 sc1 st1 Full name General Purpose solid-state drives (SSD) Provisioned IOPS SSD. Cold hard disk drive (HDD) volume. Throughput optimized hard disk drive (HDD) volume. Ideal for A broad range of transactionl workloads. - Low latency is a must.
- IOPS-intensive workloads.
- Mission-critical workloads.
- Performance-intensive workloads.
Infrequently accessed, throughput-intensive workloads with large datasets and large I/O sizes Frequently accessed, throughput-intensive workloads with large datasets and large I/O sizes. Merits - Indefinitely sustain their full provisioned IOPS and throughput performance.
- Cost-effective.
- Provided low latency.
- Highest performance for EBS.
- Can be attached to multiple EC2 instances.
Low-cost magnetic storage. - Low cost.
- Higher throughput than SC1.
Examples - Virtual desktops.
- Medium-sized single instance databases.
- Latency sensitive interactive applications.
- Development and test environments.
MySQL, MongoDB.
— Ref.- Log processing.
- Hadoop clusters.
- Windows File Server.
- big data workloads with large data sets.
- ETL.
- Kafka.
- Amazon EMR.
- Log processing.
- Data warehouses.
- They are deleted on EC2 instance termination, unless you configure them to not to.
- EBS snapshot:
- Taking backup.
- When you wanna take a backup/snapshot it is recommended to detach EBS volume first.
- You can move snapshots between regions.
- Can be used for disaster recovery: Take snapshot in region1 and them copy it in several regions, then when needed just restore them.
- Archive snapshots.
- Cheaper.
- They need more time to be restored (up to 3 hour).
- Recycle bin.
- Define a retention rule.
- Retention rule: For how long we wanna keep the deleted snapshot.
- Can increase the size of created EBS volume from snapshot.
-
EC2 instance store
- A physical hard drive installed on the hardware that our EC2 instance is running on.
-
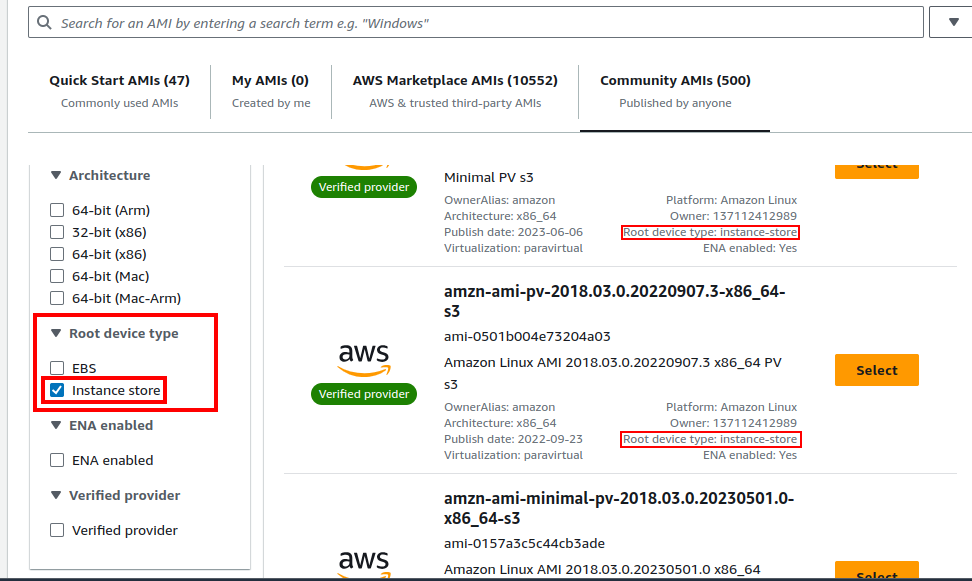
You need to go to the “Community AMIs” when browsing for an OS with instance type storage:
- Better I/O:
- High throughput.
- High disk performance.
- Ephemeral:
- Stopping or terminating EC2 = Losing data.
- Good for buffer, cache, temp data.
- We can get backup from them.
- Better I/O:
-
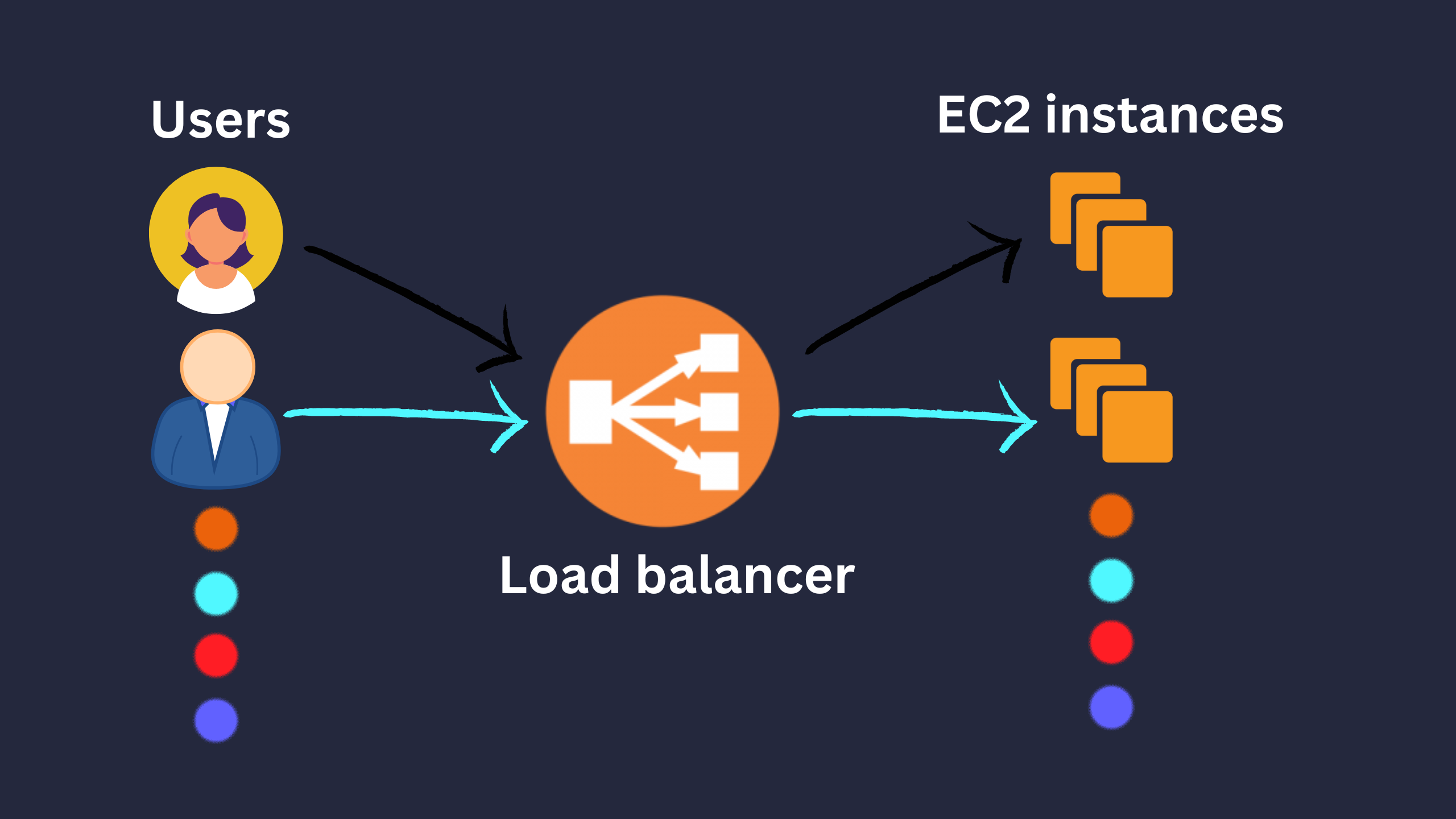
Load balancer:
- Manged service.
- What we’ll expose publicly.
-
Forwards internet traffic to multiple EC2 instances.
- What it does for us:
- Load spreading.
- SSL termination.
- Performs regular health checks.
- Provides a single point of access (DNS).
- Won’t send load to unhealthy EC2 instances.
- High-availability across zones by having one load balancer.
- It is cheaper to have an on-premise1 load balancer.
-
It can be:
Network Load Balancer Gateway Load Balancer Application Load Balancer AKA GLB NLB ALB Works on which OSI layer Layer 3: GENEVE protocol Layer 4: TCP/UDP protocol Layer 7: HTTP, HTTPS, RPC protocol Known for Routing traffics to my firewalls (on EC2 instances) to detect intrusion for example. Its high performance: it can route millions of requests per second. HTTP routing features. Requirements A separate EC2 instance where checks the requests. Static IP Static DNS Infographic 


- To create a load balancer:
- Create a security group (based on IP, port, or protocol).
- Create a target group (instances we wanna load balance).
-
# Elastic Load Balancing (ELB):
- Distributes the workload between EC2 instances in an ASG.
-
Learn more about ASG here
Local zones
Shared responsibility model
| AWS | User |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure. | Security group rules. |
| Replacing faulty hardware. | OS maintenance. |
| Compliance validation. | Data security. |
| Data replication for EBS. | IAM roles/users (Access management). |
Footnotes
-
Self-hosted or on an EC2 instance. ↩