Execution from inside
- Each field defined in a type system behaves like a function.
- Each field returns the next type.
-
Each field on each type is backed by a resolver function.
-
E.g. when here we are returning a
RandomDieand inside that type we haverollandrollOncewhich are also considered resolvers.Though we never really passed them explicitly as resolver to our
rootApivariable.
-
- The execution stops when you return a scalar/enum type – like
Todoobject type.

Resolvers
# A resolver function receives 4 arguments in this specific order:
async function getTodo(
/**
* @description
* The previous object.
*
* - AKA root, or parent.
* - A GraphQL server needs to call the resolvers of a query’s fields. GraphQL does a breadth-first (level-by-level) resolver call. The root argument in each resolver call is simply the result of the previous call.
* - Mostly won't be used.
*/
obj,
/**
* @description
* Arguments/parameters passed to a field in a GraphQL operation.
* @example `getTodo(id: ID!)`
*/
args: { id: string },
/**
* @description
* An object that every resolver can write to and read from it so that resolvers can communicate.
*
* Holds important contextual information, things like:
* - Access to a database.
* - The currently logged in user.
*/
context: { db: PrismaClient },
/**
* @description
* The Abstract Syntax Tree representation of a query or mutation.
*
* Holds field-specific* info and the schema details.
*
* *Things relevant to the current operation.
*/
info,
) {
const todo = await context.db.todo.find({
where: { id: args.id },
});
const graphqlTodoObject = new GraphqlTodo(todo);
return graphqlTodoObject;
}
class GraphqlTodo {
public id: string;
public title: string;
public content: string;
public createdAt: Date;
public updatedAt: Date;
public CreatedBy: { id: string; username: string };
public createdById: string;
public AssignedTo: { id: string; username: string };
public assignedToId: string;
constructor(todo: PrismaTodo) {
this.id = todo.id;
this.title = todo.title;
this.content = todo.content;
this.createdAt = todo.createdAt;
this.updatedAt = todo.updatedAt;
this.CreatedBy = todo.CreatedBy;
this.createdById = todo.createdById;
this.AssignedTo = todo.AssignedTo;
this.assignedToId = todo.assignedToId;
}
}
An Important Note About args in a Resolver

— Ref.
[!NOTE]
I’ve demystified the
infoobject in GraphQL here.
# No Need to Define Trivial Resolvers Like getTodoName
import { GraphQLResolveInfo } from 'graphql';
function getTodoName(
obj: GraphqlTodo,
args,
context,
info: GraphQLResolveInfo,
) {
return obj.name;
}
Most of the times when we have not defined a resolver the lib we’re using to build our GraphQL service assume that there is a property/method named exactly the same as the field. Thus it automatically calls that one.
What is AST
- Stands for Abstract Syntax Tree.
- A data structure.
- A very broad term used in computer science (wiki).
- Represents the structure of a program, code snippet, or a GraphQL query.
- A tree representation of the abstract syntactic structure of text (often source code, but here a GraphQL query) written in a formal language.
- Formal language essentially is a language that consciously and deliberately is designed to express a set of particular concepts without ambiguity.
- # In GraphQL a query comes in as a string, this string must be split into meaningful sub-strings and parsed into a representation that the machine understands.
Tokenization
- A lexical token is a string with an assigned and thus identified meaning, in contrast to the probabilistic token used in large language models. AKA lexing (or lexical analysis).
- Here you can find out about the rules the GraphQL lexer uses to tokenize your query.
- Here is our lexer in
graphql.
A GraphQL Query Parts After Tokenization

- Its root is called
Document. - A
Documentcan have one or manyDefinition.- A Definition is either:
- A
OperationDefinition. - Or
FragmentDefinition.
- A
- It contains at least one
OperationDefinition.
- A Definition is either:
-
An
OperationDefinitionis:-
The
OperationTypefollowed by an optional givenName.- E.g.
query GetUsers...
- E.g.
-
Then usually we define our
SelectionSet.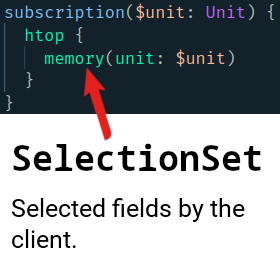
It accepts more than this and you can see a complete list here.
-
- You can see here how
graphql’s parser usesLexerto parse a GraphQL query.