Learn more
</dd>
#
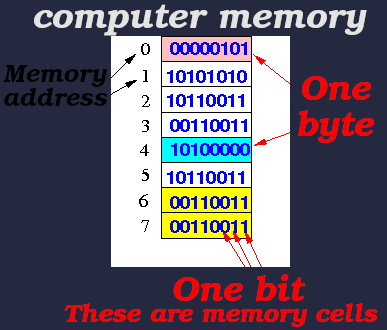
Memory cell
An electronic circuit.
Stores one bit of binary information.
Stores a logic 1 (high voltage level) and reset to store a logic 0 (low voltage level).
 #
f-strings
String literals that have embedded expressions.
#
f-strings
String literals that have embedded expressions.
name = "Fred"
f"He said his name is {name}."
Learn more here.
#
Arithmetic progressions
A sequence of numbers in which the difference between consecutive terms is constant.
General formula: a, a+d, a+2d, a+3d, ...
a is the first term.
Fixed difference is called the common difference (represented as d).
Positive common difference example sequence: 3, 7, 11, 15, 19, ...
Negative common difference example sequence: 20, 15, 10, 5, 0, ...
#
docstring
Short for documentation string.
A special string used to document a module, class, or function in Python.
Stored as part of the function’s metadata.
#
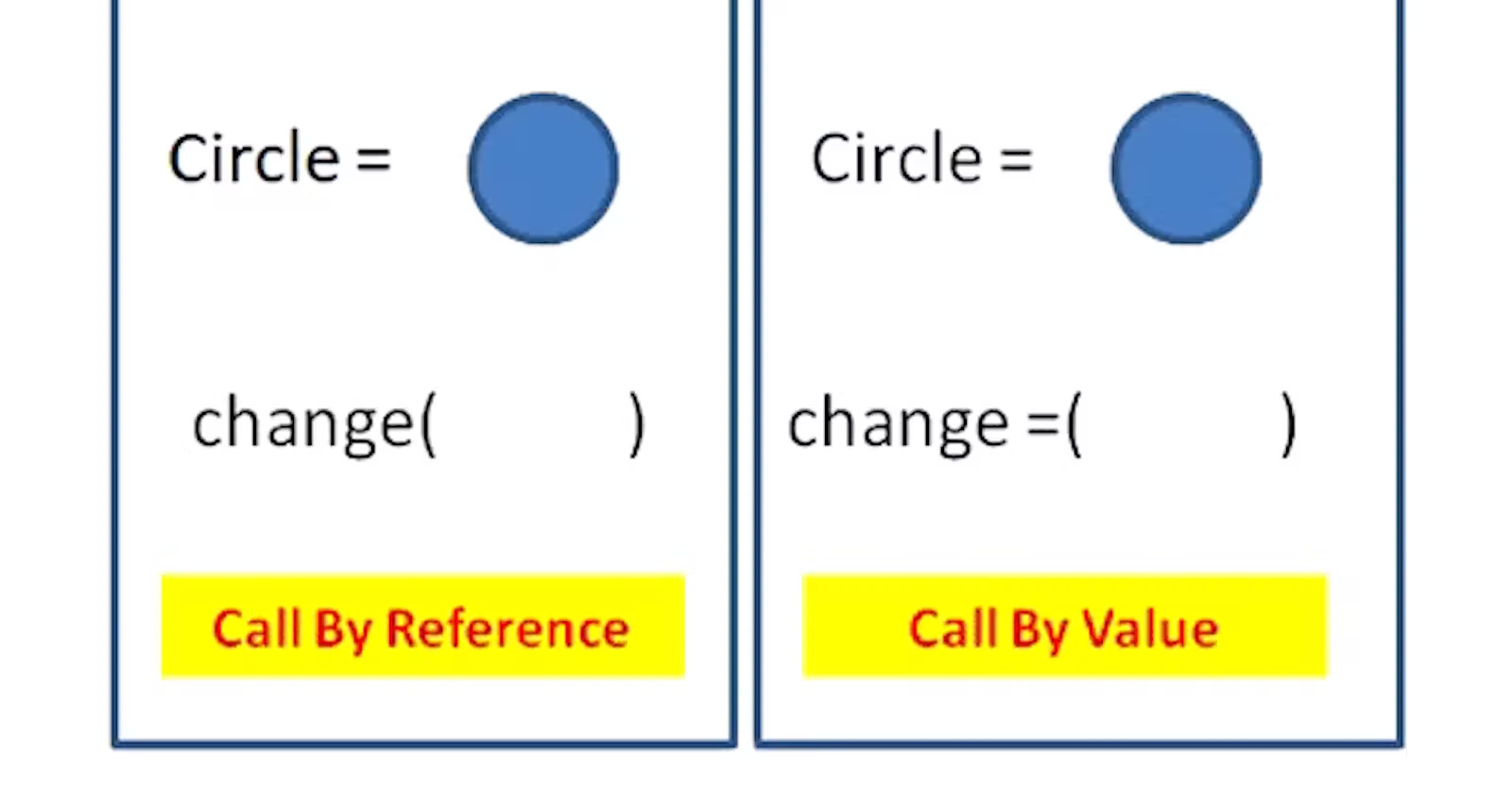
Call by reference
The value is always an object reference, not the value of the object.
robot = {}
def deactivate(p):
p['active'] = False
print("Robot before function call: ", robot)
deactivate(robot)
print("Robot after function call: ", robot)
Check this to understand it better
#
Call by value
The actual parameters are evaluated and their values are copied to the callee.
color = 'purple'
def some_func(p):
p = 'turquoise'
print("Before: ", color)
some_func(color)
print("After: ", color)
Check this to understand it better
</dl>
## Call by Value VS Call by Reference