Lambda Expressions

- Small anonymous functions.
- Can take any number of arguments, but can only have one expression.
- Aliases:
- Function literals.
- Anonymous functions (what we usually call them in JS).
- Lambda form.
- Lambda functions (what we usually call them in Python).
- Lambda expressions.
- Lambda abstractions.
[!NOTE]
It is a concept borrowed from functional programming paradigm.
- In Python lambdas are only a shorthand notation, if you’re too lazy to define a function (ref) you can use lambda function.
- Keep in mind to NOT expect anything fancy from them.
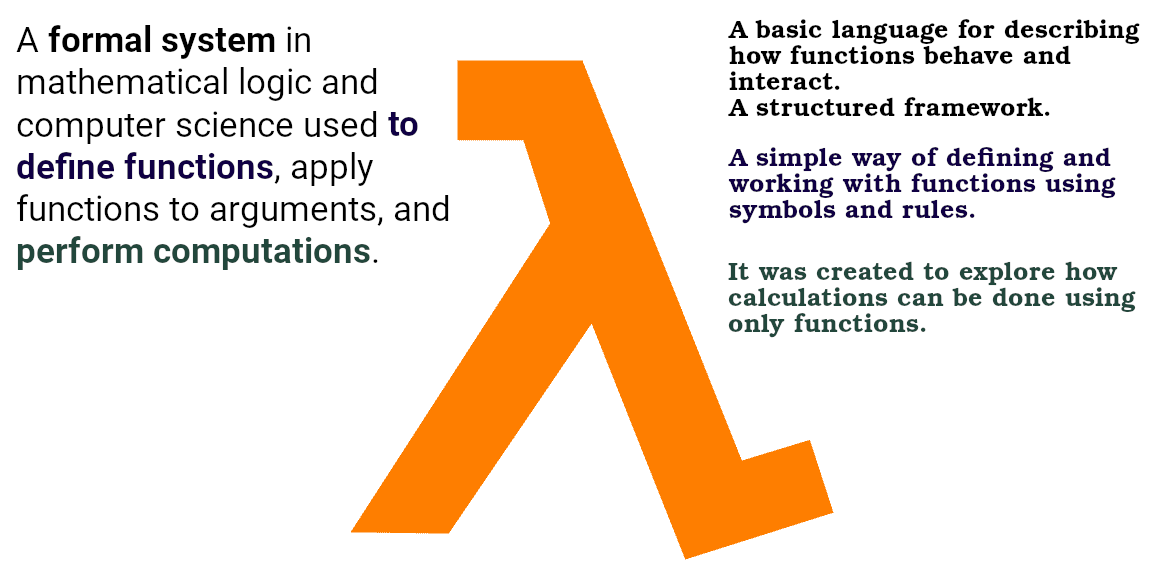
Lambda Calculus
Lambda functions in Python and other programming languages originates from Lambda Calculus. Here is a formal definition of it + a breakdown:
Syntax
- Created with the
lambdakeyword. - Used wherever function objects are required.
- Syntactically restricted to a single expression.
- No statement is allowed inside it.
- Does NOT support type annotations.
- Just syntactic sugar for a normal function.
- Frequently used with higher-order functions.
- It either:
- Takes one or more functions as arguments.
- Or returns one or more functions.
- E.g.
map(),filter(),functools.reduce(), etc:fruits = ['pineapple', 'banana', 'cherry'] res = list(map(str.upper, fruits)) print(res)
- It either:
lambda arguments : expression
Examples
def make_incrementor(n):
return lambda x: x + n
temp = make_incrementor(13) # temp = lambda x: x + 13
print(temp(1)) # lambda 1: 1 + 13 => 14
x = lambda a, b, c: a + b + c
print(x(1, 2, 3)) # lambda 1, 2, 3: 1 + 2 + 3
full_name = lambda first, last: f'{first.strip().capitalize()} {last.strip().title()}'
full_name(' alen ', ' kim ') # Alen Kim
list1 = [1, 2, 3]
list2 = [4, 5, 6]
sum_of_list1_and_list2_elements = list(map(lambda x, y: x + y, list1, list2))
print(sum_of_list1_and_list2_elements)
Normal Function to Lambda Function

Immediately Invoked Function Expression
- Abbreviated to IIFE.
-
(lambda x, y: x + y)(2, 3) - Cannot see any practical use case though.
Debugging
- In the context of the lambda function, Python will not provide the name of the function, but only
<lambda>. - So if an exception occurs, traceback will only shows
<lambda>.
| Lambda version | Normal Functions |
|---|---|
|